What are the RAID Modes?
A Redundant Array of Independent (or Inexpensive) Disks (RAID) is a system that utilizes multiple hard drives to share or replicate data among the disks. The benefit, depending on the selected RAID Mode (combinations of disks), is one or more of increased data integrity, fault-tolerance, throughput or capacity when compared to single drives.
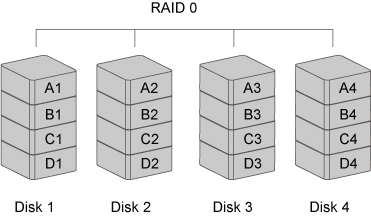
RAID 0 (STRIPING)
RAID 0 (Striping) is a performance-oriented, non-redundant data mapping technique. It combines multiple hard drives into a single logical unit. Instead of seeing several different hard drives, the operating system sees only one large drive. Striping splits data evenly across two or more disks simultaneously, dramatically increasing performance.
Striping can be implemented in disks of differing sizes, but the storage space added to the array by each disk is limited to the size of the smallest disk. Although Striping is an easily implemented, simple configuration, Striping should never be used for mission critical applications. The speed of operation is excellent in comparison to other RAID modes.
RAID 1 (Mirroring) consists of at least two drives storing duplicate copies of the same data. In this mode, the data is simultaneously written to two disks. Thus, the storage capacity of a two-disk array is combined into a single disk and the capacity is limited to the size of the smallest disk.
Spanning provides another maximum capacity solution, which some call it as "Large". Spanning combines multiple hard drives into a single logical unit. Unlike Striping, Spanning writes data to the first physical drive until it reaches full capacity. When the first disk reaches full capacity, data is written to the second physical disk. Spanning provides the maximum possible storage capacity, but does not increase performance.
CLONE consists of at least two drives storing duplicate copies of the same data. In this mode, the data is simultaneously written to two or more disks. Thus, the storage capacity of the disk array is limited to the size of the smallest disk.
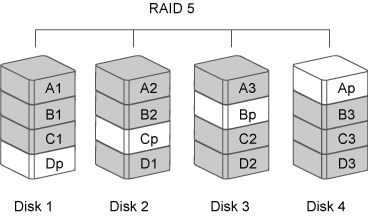
RAID 5 uses block-level striping with parity data distributed across all member disks. It is also called Parity RAID. Every time a block is written to a disk in a RAID 5 disk array, a parity block is generated within the same stripe. A block is composed of many consecutive sectors on a disk. A series of blocks (a block from each of the disks in an array) is collectively called a "stripe". The parity information inside the parity block is not the identical copy of the source data. It is generated via parity calculation. RAID 5 mode provides decent data protection and fault tolerance. The speed of operation is average in comparison to other RAID modes.
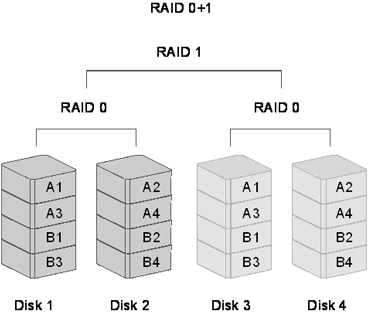
In the RAID 0+1 mode, data is organized as stripes across multiple disks. And then, the striped disk sets are mirrored. It is usually called "a mirror of stripes". RAID 0+1 mode provides excellent data protection and fault tolerance. The speed of operation is fast in comparison to other RAID modes (except in RAID 0).
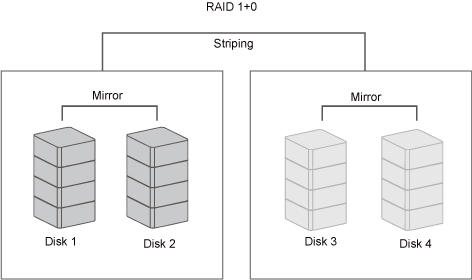
In RAID 1+0, the data is first mirrored and then striped. Under this RAID Mode, it provides another way to achieve higher performance and data security, while increasing complexity.
The key difference between RAID 0+1 and RAID 1+0 is that RAID 1+0 creates a striped set from a series of mirrored drives. In a failed disk situation, RAID 1+0 performs better because all the remaining disks can continue to be used. The array can sustain multiple drive losses as long as none of the mirror set loses all of its drives.
Just a Bunch of Disks (JBOD, also is known as "None RAID") refers to a group of hard drives. In JBOD, the number of logical drives is equal to the number of physical drives. This mode allows the RAID System to operate as a multi-disk storage enclosure, but provides no data redundancy.
HotSpare
When any of the disks in the system fails, the back up disk will automatically be rebuilt to replace the failure disk.
The DataTale™4-Bay RAID System provides the RAID 5+HotSpare, and the DataTale™4-Bay Smart RAID System provides more optional RAID modes in HotSpare, which includes RAID 1, 5, Clone, and 1+0.
RAID 0 (STRIPING)
RAID 0 (Striping) is a performance-oriented, non-redundant data mapping technique. It combines multiple hard drives into a single logical unit. Instead of seeing several different hard drives, the operating system sees only one large drive. Striping splits data evenly across two or more disks simultaneously, dramatically increasing performance.
Striping can be implemented in disks of differing sizes, but the storage space added to the array by each disk is limited to the size of the smallest disk. Although Striping is an easily implemented, simple configuration, Striping should never be used for mission critical applications. The speed of operation is excellent in comparison to other RAID modes.
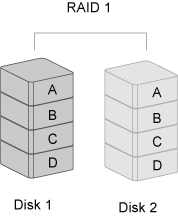
RAID 1 (Mirroring) consists of at least two drives storing duplicate copies of the same data. In this mode, the data is simultaneously written to two disks. Thus, the storage capacity of a two-disk array is combined into a single disk and the capacity is limited to the size of the smallest disk.
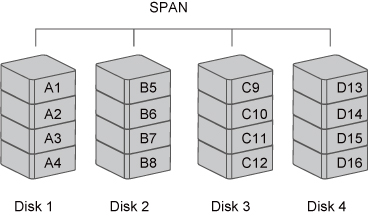
Spanning provides another maximum capacity solution, which some call it as "Large". Spanning combines multiple hard drives into a single logical unit. Unlike Striping, Spanning writes data to the first physical drive until it reaches full capacity. When the first disk reaches full capacity, data is written to the second physical disk. Spanning provides the maximum possible storage capacity, but does not increase performance.
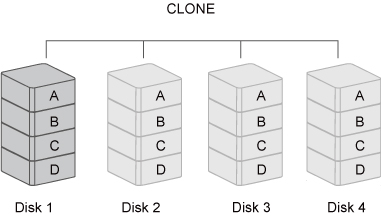
CLONE consists of at least two drives storing duplicate copies of the same data. In this mode, the data is simultaneously written to two or more disks. Thus, the storage capacity of the disk array is limited to the size of the smallest disk.
RAID 5 uses block-level striping with parity data distributed across all member disks. It is also called Parity RAID. Every time a block is written to a disk in a RAID 5 disk array, a parity block is generated within the same stripe. A block is composed of many consecutive sectors on a disk. A series of blocks (a block from each of the disks in an array) is collectively called a "stripe". The parity information inside the parity block is not the identical copy of the source data. It is generated via parity calculation. RAID 5 mode provides decent data protection and fault tolerance. The speed of operation is average in comparison to other RAID modes.
In the RAID 0+1 mode, data is organized as stripes across multiple disks. And then, the striped disk sets are mirrored. It is usually called "a mirror of stripes". RAID 0+1 mode provides excellent data protection and fault tolerance. The speed of operation is fast in comparison to other RAID modes (except in RAID 0).
In RAID 1+0, the data is first mirrored and then striped. Under this RAID Mode, it provides another way to achieve higher performance and data security, while increasing complexity.
The key difference between RAID 0+1 and RAID 1+0 is that RAID 1+0 creates a striped set from a series of mirrored drives. In a failed disk situation, RAID 1+0 performs better because all the remaining disks can continue to be used. The array can sustain multiple drive losses as long as none of the mirror set loses all of its drives.
Just a Bunch of Disks (JBOD, also is known as "None RAID") refers to a group of hard drives. In JBOD, the number of logical drives is equal to the number of physical drives. This mode allows the RAID System to operate as a multi-disk storage enclosure, but provides no data redundancy.
HotSpare
When any of the disks in the system fails, the back up disk will automatically be rebuilt to replace the failure disk.
The DataTale™4-Bay RAID System provides the RAID 5+HotSpare, and the DataTale™4-Bay Smart RAID System provides more optional RAID modes in HotSpare, which includes RAID 1, 5, Clone, and 1+0.